Indicator Gauge Icon Legend
Legend Colors
Red is bad, green is good, blue is not statistically different/neutral.
Compared to Distribution
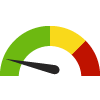 the value is in the best half of communities.
the value is in the best half of communities.
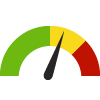 the value is in the 2nd worst quarter of communities.
the value is in the 2nd worst quarter of communities.
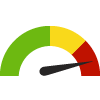 the value is in the worst quarter of communities.
the value is in the worst quarter of communities.
Compared to Target
 meets target;
meets target;  does not meet target.
does not meet target.
Compared to a Single Value
 lower than the comparison value;
lower than the comparison value;
 higher than the comparison value;
higher than the comparison value;
 not statistically different from comparison value.
not statistically different from comparison value.
Trend

 non-significant change over time;
non-significant change over time; 
 significant change over time;
significant change over time;  no change over time.
no change over time.
Compared to Prior Value
 higher than the previous measurement period;
higher than the previous measurement period;
 lower than the previous measurement period;
lower than the previous measurement period;
 no statistically different change from previous measurement period.
no statistically different change from previous measurement period.
 Significantly better than the overall value
Significantly better than the overall value
 Significantly worse than the overall value
Significantly worse than the overall value
 No significant difference with the overall value
No significant difference with the overall value
 No data on significance available
No data on significance available
Sudden Unexpected Infant Death Rate
This indicator is archived and is no longer being updated. Click to learn more
Why is this important?
Sudden unexpected infant death (SUID) is a term used to describe the sudden and unexpected death of an infant less than 1 year old in which the cause was not obvious before investigation. These deaths often happen during sleep or in the infant's sleep area (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention). Teaching caregivers about safe sleep practices is key to increasing the proportion of infants put to sleep on their backs (Healthy People 2030).
Considerations for Equitable Approaches: The rate of SUID declined considerably after safe sleep recommendations and changes to reporting requirements that started in the 1990s. Since 1999, the decline has slowed and rates have remained relatively stable. Nationally, there are disparities in SUID rates by race/ethnicity, income, and geographic location. SUID rates are highest among non-Hispanic American Indian/Alaska Native, non-Hispanic Black, and non-Hispanic Native Hawaiian/Other Pacific Islander (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention). Addressing the potential impact of structural racism and working with communities, health care, and public health professionals can help to improve understanding of effective strategies for safe infant sleep practices among various populations (American Academy of Pediatrics).Measurement period: 2011-2015
Maintained by: Conduent Healthy Communities Institute
Last update: March 2018
Data Source
- Maryland Department of Health
Maintained By: Conduent Healthy Communities Institute (Methodology)
Filed under: Health / Maternal, Fetal & Infant Health, Health Outcomes, Infants